Since GrabFood started its services in 2018, it quickly rose to the top of Southeast Asia’s food delivery market.
The tech giant was able to secure a significant share of the food delivery sector by achieving an estimated gross merchandise value (GMV) of US$5.9 billion in 2020, as reported by Momentum Works. This success was achieved despite facing tough competition from companies like foodpanda (with US$2.52 billion GMV) and gojek (with US$2 billion GMV).
While ordering and waiting for food may seem straightforward for customers, the reality behind running such a platform is quite complex.
In an exclusive webinar hosted by Grab, Xiaole Kuang, Head (Engineering Deliveries) at Grab, provides e27 with an insider’s perspective on the operational aspects of a successful food delivery platform.
Planning
Grab focuses on creating and refining its technology to offer a seamless user experience, from browsing through the platform to receiving the delivery.
The key areas of focus for Grab include: 1) localisation at scale for customers, 2) driving sustainable demand for merchant partners, and 3) maintaining a positive eater experience during peak times.
Also Read: Understanding the economics of food delivery platforms
Let’s delve deeper into how Grab prioritizes providing a delightful experience for customers, merchants, and driver partners.
For customers
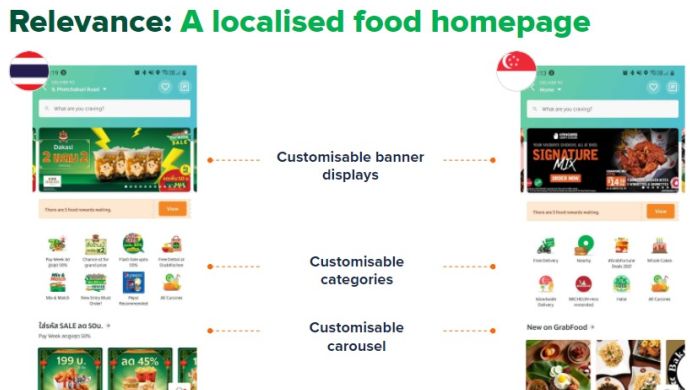
1. Hyperlocalisation
Grab aims to deliver a hyper-localized experience to users across different regions. This strategy played a significant role in Grab’s success in outshining global ride-hailing giant Uber.
To achieve hyperlocalisation, GrabFood allows country teams to customize sections on the app’s homepage based on customer consumption patterns derived from ordering habits.
Each region has its unique homepage.
2. Recommending alternative options
Similar to a restaurant steward recommending an alternative dish when a customer can’t find their favorite, Grab employs an algorithm to suggest alternative options if a particular dish is unavailable or has limited choices.
The platform also updates the “recommended for you” section with alternative food menus after users search for specific cuisines.
Also Read: Everything from soup to nuts: Meet the 27 ghost kitchen startups in Southeast Asia
3. Personalization
Unlike other food delivery apps that prioritize restaurants based solely on ratings, GrabFood provides personalized recommendations for users based on factors like browsing history, order preferences, driver availability, and estimated arrival time.
The platform lists merchants that closely match the user’s profile first.
For merchant partners
1. Ease of order handling
Grab’s merchant dashboard offers a comprehensive view of all incoming orders, regardless of type, allowing merchants to update restaurant information in real-time, such as indicating when an item is out of stock.
Additionally, merchants have access to analytics tools on the GrabMerchant app to understand customer purchasing behaviors and create targeted campaigns.
In summary, GrabFood provides an all-in-one platform for F&B business owners to manage their online operations.
2. Point of Sale integration
GrabFood introduced Point of Sale (POS) integration, allowing restaurant owners to link their POS systems with Grab, eliminating the need for manual order transfers between platforms.
Also Read: COVID-19 accelerates food delivery startups in SEA with Grab responsible for near half of growth: Report
3. Providing support
Understanding that not all merchants are tech-savvy, Grab developed a self-serve system with guides and tools to assist merchants with POS integration.
For drivers and eaters
1. Optimizing fleet batching
GrabFood utilizes an order batching system to maximize fleet efficiency during peak hours or supply shortages, ensuring multiple orders are completed in a single trip.
2. Optimizing fleet-radius reduction
In times of high demand and limited delivery riders, Grab reduces delivery radius to concentrate delivery services in a smaller area, improving order completion rates.
Also Read: In brief: Grab to create 350 new jobs in Singapore; Battery Smart raises capital
3. On-time preparation
Grab is experimenting with features to encourage merchants to prepare orders promptly, reducing wait times for drivers.
—
Image Credit: Grab
This article was originally published on March 9, 2021
The post How a great back-end tech helped GrabFood capture half of SEA’s food delivery pie despite being a latecomer appeared first on e27.
